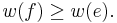Prim's algorithm
| Graph and tree search algorithms |
|---|
Search
|
| More |
Related
|
In computer science, Prim's algorithm is an algorithm that finds a minimum spanning tree for a connected weighted undirected graph. This means it finds a subset of the edges that forms a tree that includes every vertex, where the total weight of all the edges in the tree is minimized. Prim's algorithm is an example of a greedy algorithm. The algorithm was developed in 1930 by Czech mathematician Vojtěch Jarník and later independently by computer scientist Robert C. Prim in 1957 and rediscovered by Edsger Dijkstra in 1959. Therefore it is also sometimes called the DJP algorithm, the Jarník algorithm, or the Prim-Jarník algorithm.
Contents |
Description
The only spanning tree of the empty graph (with an empty vertex set) is again the empty graph. The following description assumes that this special case is handled separately.
The algorithm continuously increases the size of a tree, one edge at a time, starting with a tree consisting of a single vertex, until it spans all vertices.
- Input: A non-empty connected weighted graph with vertices V and edges E in which the weights are non-negative.
- Initialize: Vnew = {x}, where x is an arbitrary node (starting point) from V, Enew = {}
- Repeat until Vnew = V:
- Choose an edge (u, v) with minimal weight such that u is in Vnew and v is not (if there are multiple edges with the same weight, any of them may be picked)
- Add v to Vnew, and (u, v) to Enew
- Output: Vnew and Enew describe a minimal spanning tree
Time complexity
| Minimum edge weight data structure | Time complexity (total) |
|---|---|
| adjacency matrix, searching | O(V2) |
| binary heap (as in pseudocode below) and adjacency list | O((V + E) log(V)) = O(E log(V)) |
| Fibonacci heap and adjacency list | O(E + V log(V)) |
A simple implementation using an adjacency matrix graph representation and searching an array of weights to find the minimum weight edge to add requires O(V2) running time. Using a simple binary heap data structure and an adjacency list representation, Prim's algorithm can be shown to run in time O(E log V) where E is the number of edges and V is the number of vertices. Using a more sophisticated Fibonacci heap, this can be brought down to O(E + V log V), which is asymptotically faster when the graph is dense enough that E is Ω(V).
Example
| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
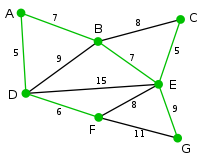
This is our original weighted graph. The numbers near the edges indicate their weight. |
 |
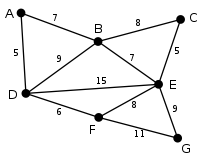
Vertex D has been arbitrarily chosen as a starting point. Vertices A, B, E and F are connected to D through a single edge. A is the vertex nearest to D and will be chosen as the second vertex along with the edge AD. |
 |
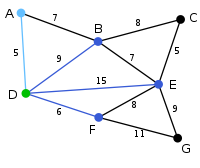
The next vertex chosen is the vertex nearest to either D or A. B is 9 away from D and 7 away from A, E is 15, and F is 6. F is the smallest distance away, so we highlight the vertex F and the arc DF. |
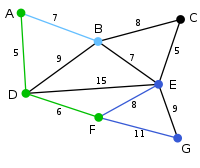 |
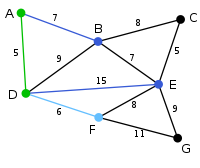
The algorithm carries on as above. Vertex B, which is 7 away from A, is highlighted. |
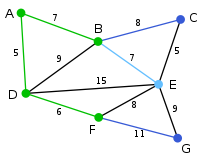 |
In this case, we can choose between C, E, and G. C is 8 away from B, E is 7 away from B, and G is 11 away from F. E is nearest, so we highlight the vertex E and the arc BE. |
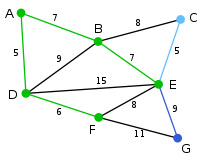 |
Here, the only vertices available are C and G. C is 5 away from E, and G is 9 away from E. C is chosen, so it is highlighted along with the arc EC. |
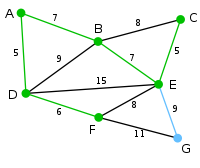 |
Vertex G is the only remaining vertex. It is 11 away from F, and 9 away from E. E is nearer, so we highlight it and the arc EG. |
 |
Now all the vertices have been selected and the minimum spanning tree is shown in green. In this case, it has weight 39. |
| U | Edge(u,v) | V-U |
|---|---|---|
| {} | {A,B,C,D,E,F,G} | |
| {D} | (D,A)=5 V (D,B)=9 (D,E)=15 (D,F)=6 |
{A,B,C,E,F,G} |
| {A,D} | (D,B)=9 (D,E)=15 (D,F)=6 V (A,B)=7 |
{B,C,E,F,G} |
| {A,D,F} | (D,B)=9 (D,E)=15 (A,B)=7 V (F,E)=8 (F,G)=11 |
{B,C,E,G} |
| {A,B,D,F} | (B,C)=8 (B,E)=7 V (D,B)=9 (D,E)=15 (F,E)=8 (F,G)=11 |
{C,E,G} |
| {A,B,D,E,F} | (B,C)=8 (D,B)=9 (D,E)=15 cycle (E,C)=5 V (E,G)=9 (F,E)=8 cycle (F,G)=11 |
{C,G} |
| {A,B,C,D,E,F} | (B,C)=8 cycle (D,B)=9 (D,E)=15 cycle (E,G)=9 V (F,E)=8 cycle (F,G)=11 |
{G} |
| {A,B,C,D,E,F,G} | (B,C)=8 cycle (D,B)=9 (D,E)=15 cycle (F,E)=8 cycle (F,G)=11 |
{} |
Pseudocode
Min-heap
- Initialization
- inputs: A graph, a function returning edge weights weight-function, and an initial vertex
Initial placement of all vertices in the 'not yet seen' set, set initial vertex to be added to the tree, and place all vertices in a min-heap to allow for removal of the min distance from the minimum graph.
for each vertex in graph set min_distance of vertex to ∞ set parent of vertex to null set minimum_adjacency_list of vertex to empty list set is_in_Q of vertex to true set min_distance of initial vertex to zero add to minimum-heap Q all vertices in graph, keyed by min_distance
- Algorithm
In the algorithm description above,
- nearest vertex is Q[0], now latest addition
- fringe is v in Q where distance of v < ∞ after nearest vertex is removed
- not seen is v in Q where distance of v = ∞ after nearest vertex is removed
The while loop will fail when remove minimum returns null. The adjacency list is set to allow a directional graph to be returned.
- time complexity: V for loop, log(V) for the remove function
while latest_addition = remove minimum in Q
set is_in_Q of latest_addition to false
add latest_addition to (minimum_adjacency_list of (parent of latest_addition))
add (parent of latest_addition) to (minimum_adjacency_list of latest_addition)
- time complexity: E/V, the average number of vertices
for each adjacent of latest_addition
if (is_in_Q of adjacent) and (weight-function(latest_addition, adjacent) < min_distance of adjacent)
set parent of adjacent to latest_addition
set min_distance of adjacent to weight-function(latest_addition, adjacent)
- time complexity: log(V), the height of the heap
update adjacent in Q, order by min_distance
Proof of correctness
Let P be a connected, weighted graph. At every iteration of Prim's algorithm, an edge must be found that connects a vertex in a subgraph to a vertex outside the subgraph. Since P is connected, there will always be a path to every vertex. The output Y of Prim's algorithm is a tree, because the edge and vertex added to Y are connected. Let Y1 be a minimum spanning tree of P. If Y1=Y then Y is a minimum spanning tree. Otherwise, let e be the first edge added during the construction of Y that is not in Y1, and V be the set of vertices connected by the edges added before e. Then one endpoint of e is in V and the other is not. Since Y1 is a spanning tree of P, there is a path in Y1 joining the two endpoints. As one travels along the path, one must encounter an edge f joining a vertex in V to one that is not in V. Now, at the iteration when e was added to Y, f could also have been added and it would be added instead of e if its weight was less than e. Since f was not added, we conclude that
Let Y2 be the graph obtained by removing f and adding e from Y1. It is easy to show that Y2 is connected, has the same number of edges as Y1, and the total weights of its edges is not larger than that of Y1, therefore it is also a minimum spanning tree of P and it contains e and all the edges added before it during the construction of V. Repeat the steps above and we will eventually obtain a minimum spanning tree of P that is identical to Y. This shows Y is a minimum spanning tree.
Other algorithms for this problem include Kruskal's algorithm and Borůvka's algorithm.
References
- V. Jarník: O jistém problému minimálním [About a certain minimal problem], Práce Moravské Přírodovědecké Společnosti, 6, 1930, pp. 57-63. (in Czech)
- R. C. Prim: Shortest connection networks and some generalizations. In: Bell System Technical Journal, 36 (1957), pp. 1389–1401
- D. Cherition and R. E. Tarjan: Finding minimum spanning trees. In: SIAM Journal on Computing, 5 (Dec. 1976), pp. 724–741
- Thomas H. Cormen, Charles E. Leiserson, Ronald L. Rivest, and Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms, Third Edition. MIT Press, 2009. ISBN 0-262-03384-4. Section 23.2: The algorithms of Kruskal and Prim, pp.631–638.